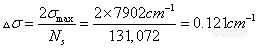![]()
where σmax is the maximum wavenumber allowed with the sample space (undersampling ratio) of 2. Therefore the actual spectral resolution is slightly higher than the software defined. Note that the average full width at half height (FWHH*) of the peaks over the entire CO band region is 0.084cm-1 (with a standard deviation of 0.002 cm-1) when spectral resolution of 0.125cm-1 is selected by OMNIC software. Thus, an actually spectral resolving capability of better than 0.09cm-1 for the natural separation of two identical lines is achieve. Figure 2.1 shows a spectrum of the standard CO sealed gas cell in the region of 2250-2000cm-1 with an expanded view of the spectrum around the peak at 2180cm-1. This spectrum was obtained with standard boxcar apodization function and a software-selected resolution of 0.125cm-1.