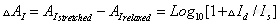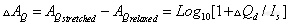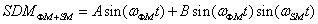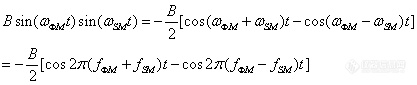These procedures yield six interferograms simultaneously from a single SDM experiment. When the phase angles for ΦM and SM modulation, θΦM, and θSM, are optimized through the use of the elastic reference as described above, only three channels, one static channel Is(I) and two dynamic channels ΔId(I,I) and ΔQd(I,Q), contain significant signals. The Is spectrum gives the static single-beam spectrum of the polymeric sample. The ΔId and ΔQd are the dynamic single-beam spectra of the polymeric sample in response to the sample modulation. ΔId and ΔQd spectra are then ratioed to Is to yield the dynamic transmission spectra, ΔId/Is, ΔQd/Is, and differential absorbance spectra ΔAI and ΔAQ for in-phase and quadrature channels are then obtained by using Equations (3-12) and (3-13):
![]()
![]()