获得0积分,您同时完成了每日任务,有额外的积分奖励,请前往APP领取
立即前往
原文由 chengjingbao(chengjingbao) 发表:原文由 enslyde(enslyde) 发表:原文由 独钓寒江雪(hzhhqt) 发表:
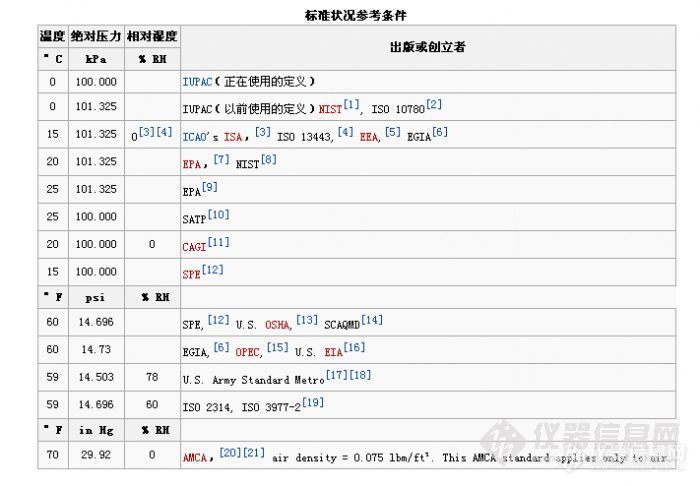
“注一个:标准状态就完了,其温度都不知道,更如何得知其密度呢?”
标准状态就是:0℃和101.325kPa
所以不需要再说温度和压强了
标准状态的定义 请百度一下,定义有变化,标准也不一样。
不要过于迷信百度,正规的图书和资料中有.